学习提要
必备插件
VSCode 开发安装插件
- Vetur – Pine Wu
- Vue 3 Snippets – hollowtree
学习内容
后端开发人员学 Vue,因此重点在学会怎么用,学会常用的组件库。
- Vue 的基本语法,生命周期,各种属性的含义
- 为 DOM 绑定事件,给绑定的方法传递参数
- 不同 vue 组件的参数传递
- 父组件传递数据给子组件 – props 属性
- 子组件传递数据给父组件 –
this.$emit触发父组件的事件,通过触发事件,将参数传递给事件的函数,从而进行参数传递。 - 兄弟组件传递数据 – 单独将状态提出来做管理或者 vuex,pinia。
- 路由组件 – vue-router
- 全局状态管理组件 – vue-router
- 缓存(StoreSession)
- 如何发起 ajax 请求
版本选择
- 开发版本,有完整的警告和调试模式
- 生成版本,删除了警告
- CDN,用于快速学习
ESLint
- 声明但是未使用的变量会报错
- 空行不能连续大于等于 2
- 在行结尾处,多余的空格不允许
- 多余的分号,不允许
- 字符串要使用单引号,不能使用双引号
- 在方法名和形参列表的小括号之间,必须有一个空格
- 在单行注释的 // 之后,必须有一个空格
- 在每一个文件的结尾处,必须有一个空行
- import 语句必须放到最顶部
- etc…
vue2入门
入门例子
下面为 vue2 的一个基本示例,展示了如何创建 Vue 对象,将 Vue 绑定到 DOM 上,以及 if-else,for 的语法。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h4></h4>
<li>
<!-- 就是 if-else -->
<span v-if="!item.del">未删除 </span>
<span v-else>删除了 </span> <br />
<!-- 为 true 就显示 -->
<span v-show="item.show">显示!</span>
</li>
<h4>for 循环用法</h4>
<!-- 循环遍历 -->
<li v-for=" item in list">
<span></span><br>
</li>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 创建一个 vue 对象,这个对象绑定到 id 为 app 的 dom 上
// data 为在 dom 中需要使用的数据
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'hello world',
item: {
title: 'some',
del: false,
show: true
},
list: [{
name: 'tom'
}, {
name: 'jetty'
}]
}
})
</script>
</html>
组件注册
如果我们在 html 中需要多次用到同样的东西,我们可以把它抽取成一个『组件』,然后进行 html 块的复用。
- 使用 Vue.component(‘组件名’, { }); 注册组件
- 在 html 中直接通过 <组件名> 使用标签
组件的定义及使用如下。
<body>
<div id="app">
<h4>组件</h4>
<div v-for=" item in list">
<todo-item :title="item.name" :del="true" :show="true"></todo-item>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.component('todo-item', {
// 组件中的具体内容(即 html)
template: `<li><span v-if="!del">未删除 </span><span v-else>删除了 </span> <br /></li>`,
// 为组件定义一些属性(为类定义属性值),直接传递属性给组件
props: {
title: String,
del: {
type: Boolean,
default: false
},
},
// 组件内部的数据, 要返回(return),也可以 data(){ return{} } 这样写,一样的效果。
data: function() {
return { name: '123'};
},
// 组件内部用到的一些方法,如点击事件
methods: {},
})
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'hello world',
list: [{ name: 'tom'}, { name: 'jetty' }]
}
})
</script>
</html>
绑定事件
- 给原生 DOM 绑定事件 – @click=‘function’,很简单,就不写 Demo 了。
- 给组件绑定事件并调用,调用涉及到父子通信,需要用到
this.$emit方法。此处假定的逻辑是,子组件触发 click 方法后,调用父组件的 @delete 将两个参数传递给父组件。
<body>
<div id="app">
<h4>组件</h4>
<todo-list></todo-list>
</div>
</body>
<script>
// 子组件
Vue.component('todo-item', {
// 组件中的具体内容(即 html)
template: `<li><span></span><button @click='delData'>删除</button></li>`,
props: { title: String },
// 组件内部用到的一些方法,如点击事件
methods: {
delData(args) {
console.log("删除数据", args);
// 假定处理逻辑是:子组件点击删除事件后,触发父组件的 delete 事件
this.$emit('delete', 1, 2);
}
},
});
// 父组件
Vue.component('todo-list', {
// 父组件通过 :title 把自己的数据传递给子组件
template: `<div><todo-item @delete='handleDel' v-for="item in list" :title="item.name"></todo-item></div>`,
data() {
return {
list: [{ name: 'tom' }, { name: 'jetty' }]
}
},
methods: {
handleDel(arg1, arg2) {
console.log("触发了父组件的 @delete 事件", arg1, arg2);
}
}
})
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'hello world',
}
});
</script>
</html>
事件修饰符
插槽(填充标签)
插槽:定义子组件的时候,在子组件内刨了一个坑,父组件想办法往坑里填内容。
例如,我们用 todo-item 组件,我们希望可以在这个标签填充一些其他标签。
<todo-item>
<!-- vue 2.6 的用法 -->
<template v-slot:pre-icon>前置</template>
<template v-slot:suf-icon>后置</template>
</todo-item>
<script>
Vue.component('todo-item', {
// 组件中的具体内容(即 html)
template: `<li>
<slot name='pre-icon'></slot>
<span></span>
<slot name='suf-icon'></slot>
<button @click='delData'>删除</button>
</li>`,
props: {
title: String,
},
methods: {
delData(args) {
console.log("删除数据", args);
// 子组件点击删除事件后,触发父组件的 delete 事件,删除 todo-item
this.$emit('delete', 1, 2);
}
},
</script>
完整代码
<body>
<div id="app">
<todo-list></todo-list>
</div>
</body>
<script>
// 子组件
Vue.component('todo-item', {
// 组件中的具体内容(即 html)
template: `<li>
<slot name='pre-icon'></slot>
<span></span>
<slot name='suf-icon'></slot>
<button @click='delData'>删除</button>
</li>`,
props: {
title: String,
},
methods: {
delData(args) {
console.log("删除数据", args);
// 子组件点击删除事件后,触发父组件的 delete 事件,删除 todo-item
this.$emit('delete', 1, 2);
}
},
});
// 父组件
Vue.component('todo-list', {
template: `<div>
<todo-item @delete='handleDel' v-for="item in list" :title="item.name">
<template v-slot:pre-icon>前置</template>
<template v-slot:suf-icon>后置</template>
</todo-item>
</div>`,
data() {
return {
list: [{ name: 'tom' }, { name: 'jetty'}]
};
},
methods: {
handleDel(arg1, arg2) {
console.log("触发了父组件的 @delete 事件", arg1, arg2);
}
}
})
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'hello world',
}
});
</script>
</html>
我们也可以向插槽传递属性(父组件向子组件的插槽传递属性)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<todo-list></todo-list>
</div>
</body>
<script>
// 子组件
Vue.component('todo-item', {
// 组件中的具体内容(即 html)
template: `<li>
<slot name='pre-icon' :value='123'></slot>
<span></span>
</li>`,
props: {
title: String,
}
});
// 父组件, 注意写法 v-slot:pre-icon='{value}' 这是为了后面 取出 value 值用。
Vue.component('todo-list', {
template: `<div>
<todo-item v-for="item in list" :title="item.name">
<template v-slot:pre-icon='{value}'>前置</template>
</todo-item>
</div>`,
data() {
return {
list: [{ name: 'tom'}, { name: 'jetty'}]
};
}
})
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'hello world',
}
});
</script>
</html>
单文件组件
优点
- 有语法高亮
- 便于管理(名字不容易冲突)
- 支持 CSS
- 有构建步骤,可以使用预处理器
ES6 导入导出
- 默认导入和导出
//xxx.js
let a = 10
// 默认导入
import m1 from './js/xxx.js'
// 在webpack中,每个js文件都是独立的模块
// 每个模块都有独立的作用域
// 其他模块,默认无法直接访问当前模块中定义的成员。
console.log(m1)
//xxx.js
let a = 10
let b = 20
// 这个export default{} 语法叫做默认导出。
// 在一个模块中,仅允许导出一次
export default {
a: a,
// 属性值和属性名一直可以简写。
b,
say(){
console.log("hello")
}
}
- 按需导入和导出
// 按需导入
import { 成员名称 } from '模块名'
//eg
import m2,{xx} from "xxx.js"
// as 取别名
import m2,{test1 as myTest} from "xx.js"
// 按需导出
export var a = 10
单文件组件开发
-
安装 node,百度即可
-
安装 vue cli
npm install -g @vue/cli # -g 表示全局安装 # or yarn global add @vue/cli -
创建 vue 项目 – 命令行创建
vue create vue-project # 选择默认模式 #======================================== Vue CLI v5.0.8 ? Please pick a preset: Default ([Vue 3] babel, eslint) > Default ([Vue 2] babel, eslint) Manually select features #======================================== -
创建 vue 项目 – ui 创建
vue ui 🚀 Starting GUI... 🌠 Ready on http://localhost:8000然后按根据页面的提示创建项目就行
Vue 文件结构说明
每个 .Vue 文件,都是一个 vue 组件(叫做单文件组件),它由三部分组成:
- template 结构
- script 行为
- style 样式
定义组件 Demo
<template>
<div>
<h3>这是组件Home </h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data() {
return { msg: "hello vue" }
},
methods: {},
filters: {}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
h3 {
color: bisque;
}
</style>
定义组件
- 声明一个Vue文件
<template>
<div>
<h3>这是Son 组件</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Son"
}
</script>
- 把这个组件注册为全局组件或私有组件
全局组件
import Home from "@/components/Home";
import Vue from "vue";
Vue.component('Home', Home)
私有组件
import Son from "./Son"
console.log(Son.name);
export default {
name: "Home",
data() {
return { msg: "hello vue" }
},
methods: {},
filters: {},
// 定义私有组件
components: {
'my-son': Son
}
}
组件化Vue
可以认为组件是特殊的 Vue 实例
组件和实例的相同和区别:
- 组件的 data 必须是一个 function 并 return 一个 字面量对象; 在 Vue 实例中,实例的 data 既可以是对象,也可以是方法;
- 组件中,直接通过 template 属性来指定组件的 UI 结构; 在 Vue 实例中,通过 el 属性来指定实例控制的区域;但是实例也可以使用 template;
- 组件和实例,都有自己的生命周期函数,私有的过滤器,methods 处理函数;
为什么组件中的 data 必须定义为一个方法并返回一个对象
因为这样,能够保证每次创建的组件实例,都有自己的一块唯一的数据内存,防止组件之间数据的干扰。
组件样式控制
父组件的样式会影响子组件,如何解决?
默认情况下,组件中定义的样式是全局生效的。如何样式只在当前组件内生效?
给 style 加上 scope 属性,即可。如何做到的?只要为组件添加了 scope 那么当前组件(不包括引入的组件)所有的 标签 都会使用同一个属性。
<style scope> </style>
组件数据通信
父传子
在父组件中,以标签形式使用子组件时,可以通过属性绑定,为子组件传递数据。
在子组件中,如果向父组件传递过来的数据,必须先定义 props 数组来接收
接收完 props 数据,可以直接在子组件的 template 区域使用
代码
子组件
<template>
<div>
<button @click="objFromParent.a++">a自增</button>
<h1>子组件---->-----> </h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import _ from 'loadsh'
export default {
name: "Son",
// 而 data 中的数据 可读可写
data() {
// 建议使用转存的数据,以便满足修改的请求。
// 对于对象类型的数据, 存储的是地址值,我们需要把数据拷贝一份,不修改源数据。
// 深拷贝 安装 lodash npm install lodash -S
return {
infoFormParent: this.pmsg,
objFromParent: _.cloneDeep(this.obj)
}
},
// 子组件需要使用 props 数组,接收外界传递过来的数据,接收到的数据可以直接在Son中使用
// 通过 props 接收的数据,是只读的。不要为它们重新赋值。
props: ['pmsg', 'obj']
}
</script>
父组件
<template>
<div>
<h1>父组件</h1>
<button @click="sendData">发送数组给子组件</button>
<!--在使用组件的时候,通过 属性绑定,把数据传递给子组件-->
<my-son :pmsg="parentMsg" :obj="obj"></my-son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son from "@/components/Father2Son/Son";
export default {
name: "Parent",
data() {
return {
parentMsg: '继承我的花呗',
obj: { a: 10, b: 20 }
}
},
methods: {
sendData() {}
},
components: {
'my-son': Son
}
}
</script>
渲染调用
<template>
<div id="app">
<Parent></Parent>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Parent from "@/components/Father2Son/Parent";
import Vue from "vue";
Vue.component('Parent', Parent)
export default {
components: {Parent}
}
</script>
子传父
通过事件绑定机制,子传数据给父
父为子绑定事件,然后子把自己的数据传递过去。
父亲调用方法会接收到子的数据,这时候就得到了子的数据。
代码Demo
子组件
<template>
<div>
<h1>子组件</h1>
<button @click="btnHandler">触发func事件</button>
<button @click="btnHandler2">触发func2事件,带参数</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Son",
data() {
return {
msg: ': 我是子组件的值'
}
},
methods: {
btnHandler() {
//$emit表示触发事件 , 在子组件中,通过 this.$emit() 触发父组件 为子组件绑定的 func 事件。
// func 是父组件为子组件绑定的事件。
this.$emit('func') // 调用父组件给子组件的事件 func
},
btnHandler2() {
this.$emit('func2', this.msg) // 调用父组件给子组件的事件 func
}
}
}
</script>
父组件
<template>
<div>
<h1>父组件</h1>
<!--在使用组件的时候,通过 属性绑定,把数据传递给子组件-->
<my-son @func="show" @func2="show2"></my-son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son from "@/components/Son2Father/Son";
export default {
name: "Parent",
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
show(){
console.log("有人调用了父组件的show方法!")
},
show2(args){
console.log("父组件的 show2 带有参数"+args)
}
},
components: {
'my-son': Son
}
}
</script>
兄弟传兄弟
思路
定义一个公共的Vue实例,如 bus.js 实例名称为 bus。
数据发送方,调用 bus.$emit() 触发 bus 上的某个事件,从而把数据发送出去。
在数据接收方,使用 bus.$on() 自定义事件,并指定事件处理函数。
代码示例
公共Vue实例 bus.js
import Vue from 'vue'
const bus = new Vue()
export default bus
发送数据方
<template>
<div>
<h1>哥哥</h1>
<button @click="sendMsgToDD">哥哥给弟弟数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import bus from './bus'
export default {
name: "GG",
data() {
return {
msg: '哥哥有糖给弟弟'
}
},
methods: {
sendMsgToDD() {
// 在数据发送方,调用bus.$emit() 触发 bus 上的某个事件,从而把数据发送出去
bus.$emit('ooo', this.msg)
}
}
}
</script>
接收数据方
<template>
<div>
<h3>弟弟</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import bus from './bus'
export default {
name: "DD",
data() {
return {}
},
created() {
// 在数据接收方 使用 bus.$on 自定义事件,并指定事件处理函数
bus.$on('ooo', data => {
console.log("弟弟拿到了哥哥的数据,哥哥的数据是:"+data)
})
}
}
</script>
使用 this.$refs 来获取元素和组件
基本使用
1.把要获取的 DOM 元素,添加 ref 属性,创建一个 DOM 对象的引用,指定的值,就是引用的名称
<p ref="myP">这是父组件</p>
2.如果要获取某个引用所对应的 DOM 对象,则直接使用 this.$refs.引用名称
console.log(this.$refs.myP)
3.也可使用 ref 为组件添加引用;可以使用 this.$refs.组件名称,拿到组件的引用,从而调用组件上的方法和获取组件 data 上的数据
this.$refs 获取 DOM
<template>
<div>
<!-- 通过 ref 获取到的 DOM 元素的引用,就是一个元素的 DOM 对象 -->
<h3 id="h3" @click="getContent" ref="myh3">123</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home1",
methods: {
getContent() {
// 不要在vue中操作 DOM
// console.log(document.getElementById("h3").innerHTML);
console.log(this.$refs.myh3)
}
}
}
</script>
ref 直接引用组件并调用组件的方法和数据 ★★★★★
可以使用 ref 属性直接调用子组件的方法属性!
实现父调用子的方法
<template>
<div>
<!-- 通过 ref 获取到的 DOM 元素的引用,就是一个元素的 DOM 对象 -->
<h3 id="h3" @click="getContent" ref="myh3">123</h3>
<my-son ref="son"></my-son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son from "@/components/GetDocumnet/Son"
export default {
name: "Home1",
methods: {
getContent() {
// 不要在vue中操作 DOM
// console.log(document.getElementById("h3").innerHTML);
console.log(this.$refs.myh3)
this.$refs.son.add()
}
},
components: {
"my-son": Son
}
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h3>这是Son组件 </h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Son",
data() {
return {
sonMsg: 0
}
},
methods: {
add() {
this.sonMsg++;
}
}
}
</script>
触发组件更新(原理)
Vue 是如何触发组件更新的?
Vue 是数据驱动的,数据改变的时候视图才会改变。
状态 data vs 属性 props
- 状态是组件自身的数据(即 data() { return {} })
- 属性是来自父组件的数据(子组件定义属性,然后父组件通过
:属性名将父组件的值传递给子组件) - 状态的改变未必会触发更新(只有状态在 DOM 中才会触发更新)
- 属性的改变未必会触发更新(只有属性在 DOM 中才会触发更新)
响应式更新
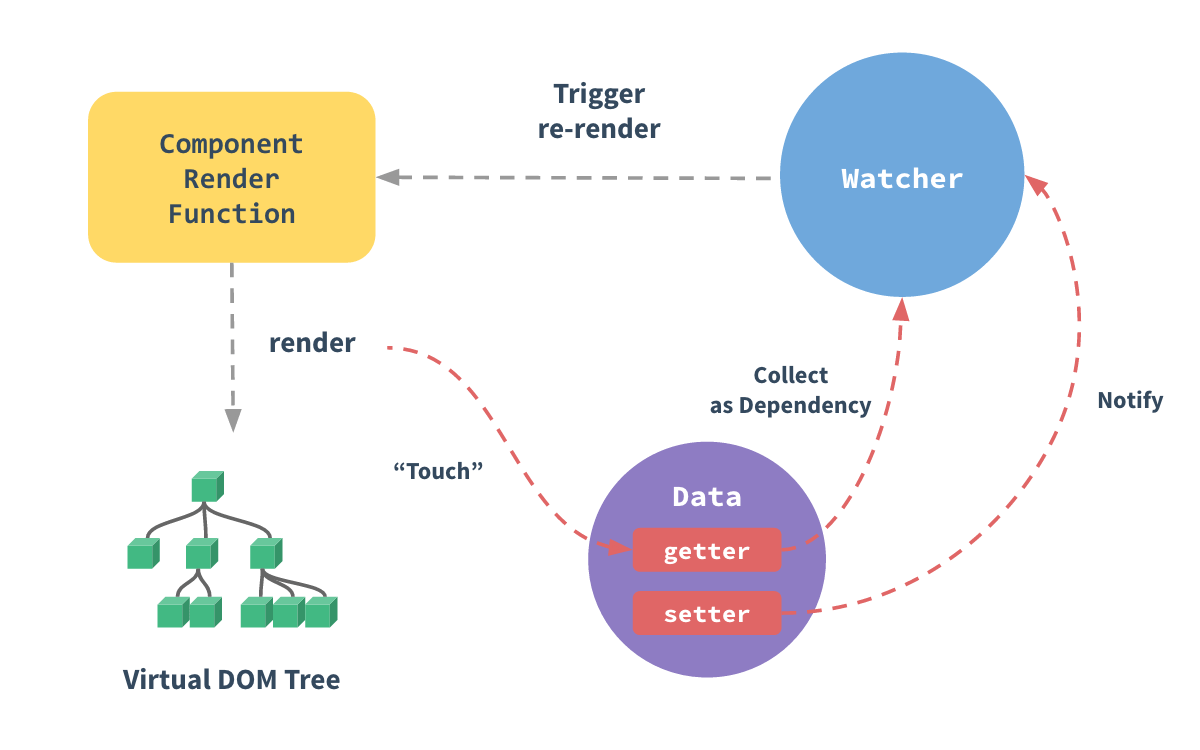
vue 在实例化的时候,会对 data 下的数据做一个 getter/setter 的转换。即,在操作数据的时候,都会经过一个代理层,而代理层是通过 getter/setter 操作数据的。
每个组件实例都对应一个 watcher 实例,它会在组件渲染的过程中(虚拟 DOM 中用到的数据)把“接触”过的数据 property 记录为依赖。之后当依赖项的 setter 触发时,会通知 watcher,从而使它关联的组件重新渲染。
例如,下面的代码就会触发组件重新渲染。
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- DOM 里用到了 num,因此会触发 updated 方法 -->
<div :data="num"></div>
<button @click="cc">111</button>
<!-- DOM 没有用到 c,因此不会触发 updated 方法 -->
<button @click="cc2">222</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
components: { HelloWorld },
data() { return { num: 1 } },
updated() { console.log("触发了更新"); },
methods: {
cc(){
console.log("click");
this.num = 2;
},
cc2() {
console.log("click");
this.c = 2;
}
}
}
</script>
单文件组件的注册
- 全局注册,一般写在 main.js 里,导入组件后使用 Vue.component(‘todo-list’,TodoList) 注册组件。
- 局部注册,仅在当前组件内有效,直接在 components 里注册,注册组件
TodoList.vue后,可以通过<todo-list></todo-list>标签使用。
定义全局组件
// 全局组件注册
import Vue from "./js/vue.js"
// 名称尽量小写,中间用-隔开
Vue.component("my-test", {
template: `<div> 这是我定义的组件 </div>`
})
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: { msg: 'hello ' }
})
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h5></h5>
<my-test></my-test>
</div>
</body>
</html>
定义私有组件
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app2',
data: {
info: '000'
},
components: {
// '组件名称':{/* 组件配置对象 */}
'my-test2':{
tenplate: `<div>这是私有组件my-test2</div>`
}
}
})
@ 的作用
-
@ 实际上是配置了 @ 指向项目根目录中的 src 文件夹
-
’@’ : path.join( __dirname, ‘./src’ )
组件化:从页面 UI 的角度分析,把页面中可复用的 UI 结构,抽离为单独的组件;实现 UI 的复用。
双向数据绑定
v-model 指令双向数据绑定,只要 vm 监听到 data 中任何一条数据的变化,都会重新执行 el 区域的所有指令。
<input v-mode="in_val">
| [表单输入绑定 | Vue.js (vuejs.org)](https://cn.vuejs.org/guide/essentials/forms.html#text) |
虚拟DOM
Vue 使用的虚拟 DOM,使用树形结构组织标签之前的曾经关系。在进行 for 遍历的时候,会要求绑定一个 key,如下
<div>
<li v-for="item in list" :key='item.somekey'>
<span></span><br>
</li>
</div>
有时会有人写成这种
<div>
<li v-for="(item, index) in list" :key='index'>
<span></span><br>
</li>
</div>
如果会对 list 中的数据进行添加删除,意味着每个 li 的 index 可能会发生变化,需要频繁修改 for 中的产生的 DOM,降低性能。建议在只需展示数据(数据不会变动)的场景下用 index 作为 key,其他情况下不要使用值会变动的 key。
操作DOM
计算属性和监听器
computed
必须是响应式数据才行
- 减少模板中计算逻辑
- 数据缓存
- 依赖固定的数据类型(应式数据)
- 适用场景,购物车求总价。
下面的例子展示了计算属性的优点
<!-- 在模板中写逻辑 -->
<div id="example">
</div>
<!-- 使用计算属性 -->
<div id="example">
<p>Original message: ""</p>
<p>Computed reversed message: ""</p>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: { message: 'Hello' },
computed: {
// 计算属性的 getter
reversedMessage: function () {
// `this` 指向 vm 实例
return this.message.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
})
</script>
使用方法也可以达成上述目的,但是计算属性会对结果进行缓存,计算属性是基于它们的响应式依赖进行缓存的。只在相关响应式依赖发生改变时它们才会重新求值。如果没有发生改变不会重新计算,而方法每次都要进行计算。
watch
监听数据是否发生变化(通过监听变化,来书写响应的逻辑,如密码长度检测)
<div id="watch-example">
<input v-model="question">
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/axios@0.12.0/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/lodash@4.13.1/lodash.min.js"></script>
<script>
var watchExampleVM = new Vue({
el: '#watch-example',
data: {
question: '',
},
watch: {
// 如果 `question` 发生改变,这个函数就会运行
question: function (newQuestion, oldQuestion) {
// question 发生变化的话,就执行下列代码
// some code
}
},
})
</script>
computed vs watch
- computed 能做的,watch 都能做,反之则不行(watch 更强大)
- 能用 computed 的尽量用 computed,computed 更简洁,清爽。
生命周期
生命周期:实例的生命周期,就是一个阶段,从创建到运行,再到销毁的阶段。 生命周期函数:在实例的生命周期中,在特定阶段执行的一些特定的事件,这些事件,叫做生命周期函数;
生命周期函数 = 生命周期钩子 = 生命周期事件
生命周期函数
- 创建期间的生命周期函数:(特点:每个实例一辈子只执行一次)
beforeCreate:创建之前,此时 data 和 methods 尚未初始化- created(第一个重要的函数,此时,data 和 methods 已经创建好了,可以被访问了,首页数据的请求一般在这里发起!)
beforeMount:挂在模板结构之前,此时,页面还没有被渲染到浏览器中(如果想初始化一些第三方的 JS 插件,必须在 mounted 中进行初始化。比如 echarts,它需要在初始化完毕的 dom 中进行操作)- mounted(第二个重要的函数,此时,页面刚被渲染出来;如果需要操作 DOM 元素,最好在这个阶段;如使用三方插件,该插件需要 DOM 初始化完毕!)
- 运行期间的生命周期函数:(特点:按需被调用至少 0 次,最多 N 次)
- beforeUpdate:数据是最新的,页面是旧的。
- updated:页面和数据都是最新的。
- 销毁期间的生命周期函数:(特点:每个实例一辈子只执行一次)
- beforeDestory:销毁之前,实例还是正常可用。
- destoryed:销毁之后,实例已经不在工作了。
| [生命周期钩子 | Vue.js (vuejs.org)](https://cn.vuejs.org/guide/essentials/lifecycle.html#lifecycle-diagram) |
函数式组件
- functional: true
- 无状态、无实例、没有 this 上下文、无生命周期
指令
常见指令
vue 中的指令,只有 `` 是用在内容节点中的,其它所有的指令,都是用在属性节点中的。
- 内容节点
<div></div> - 属性节点
<div v-html='msg'></div>
数据模板
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: "hello",
array: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
elem: "<span style='color:red'>Hello</span>"
},
method: {
show: function(){
console.log("ok");
}
}
});
</script>
v-text 基本不用
会把原来的内容清空。插值表达式只会把占位符处的数据进行解析替换。
<h3 v-text="msg">
12313
</h3>
// 显示 hello。12313会被覆盖掉的。
v-text 中使用简单的语句
<h3 v-text="msg + 666">
12313
</h3>
// 显示hello666
<h3 v-text="msg + 'abc' ">
</h3>
// 显示 hellabc
v-text 不存在闪烁问题。
场景:向元素的内容区域中,渲染指定的文本。
v-html
<h3 v-html="elem">
// 可以解析html标签
</h3>
v-bind:属性绑定;用的很频繁
为 html 属性节点动态绑定数据的,如:
<buttuon v-bind:title="mytitle">按钮</button>
应用场景:如果元素的属性值,需要动态地进行绑定,则需要使用 v-bind:指令
简写形式:
- v-bind 可以简写为
:,如 <buttuon :title="mytitle">按钮</button><img :src="boo ?img1:img2" />boo是布尔值,img1/2 是图片链接,以此动态切换图片路径
v-on:事件绑定
<div v-on:click="show">按钮</div> 绑定事件不传参
<div v-on:click="show('hello')">按钮</div> 绑定事件传参
<div @click="show('hello')">按钮</div> 简写
v-model:双向数据绑定
v-bind
v-for
v-if /v-show
自定义指令
vue 可以自定义指令,但是不推荐使用。
| [自定义指令 | Vue.js (vuejs.org)](https://cn.vuejs.org/guide/reusability/custom-directives.html#object-literals) |
// Vue.component('全局组件名称',{/* 指令的配置对象 */})
// Vue.directive("focus", { /* 指令的配置对象 */ }
自定义指令
- bind:只要指令被解析指令了,就会调用指令中的 bind 方法,其中 el 是 DOM 对象。bind 表示指令第一次被解析执行时候调用,此时,这个 DOM 元素,还没有被 append 到父节点中;
- inserted:inserted会在元素被插入到父节点后,执行,其中 el 是 DOM 对象。
- 其他诸如 updated 一类的请看官方文档。
总结:CSS 样式这类操作写在 bind 中,JS 这类操作写在 inserted 中。
Vue.directive("focus", {
bind: function (el) {
// el.focus();
// doing something
console.log(el)
},
inserted: function(el){
el.focus()
}
})
自定义指令传参
通过第二个占位符传递参数,获得参数的值通过 .value 获取
Vue.directive("focus", {
bind: function (el, param) {
// el.focus();
// doing something
el.style.color = param.value
}
})
跨层级组件获取
后期补充
常规用法
定义使用过滤器:处理文本显示格式
了解实例生命周期和生命周期函数
使用 axios 发起 Ajax 请求
- ES6 中的 Promise
- ES7 中的 async 和 await
带数据交互的案例
Vue 常见的过渡动画(不重要)
过滤器
- 过滤器的作用示例:“2020-01-23T:10:02.945Z” => 2020-01-23
- 概念:过滤器本质上是一个函数,可被用作一些常见的文本格式化。
- 过滤器只可以用在两个地方:mustache 插值表达式和 v-bind 表达式
- 过滤器应该被添加在 JavaScript 表达式的尾部,由管道符指示;
全局过滤器
-
使用全局过滤器语法
<span></span>
-
定义全局过滤器语法
Vue.filter('过滤器名称',function(originVal){ // doing something 对数据进行处理 return 处理结果; }) -
使用过滤器的注意事项
- 如果想拿管道符前面的值,通过 function 的第一个形参来拿。
- 过滤器中,一定要返回一个处理的结果,否则就是一个无效的过滤器
- 在调用过滤器的时候,直接通过() 调用就能传参;从过滤器处理函数的第二个形参开始接收传递过来的参数。
-
可多次使用 管道符,一次调用多个过滤器
全局过滤器代码示例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
传入的参数是 time,然后调用方法 dataFormat
<h3></h3>
</div>
</body>
<script>
Vue.filter('dataFormat', function (originVal) {
const date = new Date(originVal);
let years = date.getFullYear()
let month = date.getMonth() + 1
let day = date.getDay()
// 魔法字符串${}是占位符
return `${years}-${month}-${day}`;
});
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
time: '2020-01-22 23:11:23'
}
});
</script>
</html>
Promise、async、await
Promise
概念:
ES6 中的新语法,Promise 是一个构造函数;每个 new 出来的 Promise 实例对象,都代表一个异步操作。
JS 解析引擎是单线程的;宿主环境(浏览器、Node 环境)是多线程的。
异步的任务会放到异步回调函数的队列中。当 js 把自己栈中的任务执行完后,才会执行异步回调函数队列中的任务。
作用
解决了回调地狱的问题;
- 回调地狱,指的是回调函数中,嵌套回调函数的代码形式;如果嵌套的层级很深,就是回调地狱。
- 回调地狱,不利于代码的阅读、维护和后期的扩展。
Promise用法
异步代码回顾
/**
JS解析引擎是单线程的;宿主环境(浏览器、Node环境)是多线程的。
异步的任务会放到异步回调函数的队列中。当js把自己栈中的任务执行完后,才会执行异步回调函数队列中的任务。
*/
回调地狱代码示例:node.js
const fs = require('fs')
fs.readFile('./files/1.txt', 'utf-8', (err, dataStr1) => {
if (err) return console.log(err.message);
console.log(dataStr1);
fs.readFile('./files/2.txt', 'utf-8', (err, dataStr1) => {
if (err) return console.log(err.message);
console.log(dataStr1);
fs.readFile('./files/3.txt', 'utf-8', (err, dataStr1) => {
if (err) return console.log(err.message);
console.log(dataStr1);
})
})
})
Promise 不会减少代码量,但是可以解决回调地狱的问题。
创建形式上的异步操作
const p = new Promise()
创建具体的异步操作;只要 new 了就会立即执行!
// 只要new了,就会立即执行!
const p = new Promise(function(successCb,errorCb){
// 定义具体的异步操作
})
// 定义成功和失败的回调
p.then(successCallback,errorCallback);
查看下 Promise 的原型链
prototype
- catch:function catch()
- constructor:function Promise()
- finally:function finally()
- then:function then() 为 Promise 示例对象,.then() 方法最多需要两个参数,成功和失败的回调函数;它的返回值是 Promise 对象。
- catch:function catch() 捕获前面所有 .then() 中发生的错误,集中处理。
const fs = require('fs')
//==================无效写法================
function getContentByPath(fPath) {
// js主线程只负责new出这个Promise,具体的执行交给浏览器执行了
const p = new Promise(function () {
fs.readFile(fPath, 'utf-8', (err, dataStr1) => {
if (err) return console.log(err.message);
console.log(dataStr1);
// return dataStr1; 所以这个返回值是无效的。
})
})
}
getContentByPath('./files/1.txt')
//==================无效写法================
//==================有效写法================
function getContentByPath2(fPath) {
// js主线程只负责new出这个Promise,具体的执行交给浏览器执行了.回调函数从哪里来?
const p = new Promise(function (successCallback, errorCallback) {
fs.readFile(fPath, 'utf-8', (err, dataStr1) => {
if (err) return errorCallback(err);
successCallback(dataStr1)
})
});
return p;
}
const r1 = getContentByPath2('./files/1.txt')
// 成功回调 失败回调
r1.then(function (info) { console.log(info); console.log("success"); }, function (err) { console.log(err); });
//==================有效写法================
实际我们不会自己封装 Promise,会使用其他人封装的方法。
async和await
ES7 中 async 和 await 可以简化 Promise 调用,提高 Promise 代码的阅读性和理解性。
- 如果某个方法的返回值是 Promise 对象,那么,就可以用 await 关键字,来修饰 promise 实例
- 如果一个方法内部用了 await 那么这个方法必须修饰为 async 异步方法
- 精简:await 只能用在被 async 修饰的方法中
function getContentByPath(fpath){
return new Promise(function(successCb,errorCb){
fs.readFile(fpath, 'utf-8',(err,data)=>{
if(err) return errorCb(err)
successCb(data)
})
})
}
const data = await getContentByPath("./fs.txt")
// 如果一个方法内部用了await那么这个方法必须修饰为async
async function test(){
const data = await getContentByPath("./fs.txt")
}
axios
之前发起请求的方式
- 最开始封装 XMLHttpRequest 对象发起 Ajax 请求。
- 使用 Jquery 中提供的工具函数:
$.ajax({配置对象})$.post(url地址, function(){})$.get(url地址,处理函数)
- 现在,用 axios 发起 Ajax 请求。
- 只支持 get 和 post 请求,无法发起 JSONP 请求。
- 如果涉及到 JSONP 请求,让后端启用 cors 跨域资源共享即可。
- 在 Vue 中使用 vue-resource 发起数据请求
- 支持 get post jsonp ,vue 官方不推荐。
axios的使用
- 测试数据地址
- get 测试地址 http://www.liulongbin.top:3005/api/get
- post 测试地址 http://www.liulongbin.top:3005/api/post
- 使用 axios.get() 和 axios.post() 发起请求。
- 使用拦截器实现 loading 效果
- 使用 async 和 await 结合 axios 发起 Ajax 请求
get请求
使用 axios 发起 get 请求
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script src="js/axios.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<button @click='getInfo'>GET</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
methods: {
getInfo() {
const result = axios.get('http://www.liulongbin.top:3005/api/get', { params: { name: 'zs', age: 20 } });
result.then(function (res) {
console.log(res);
})
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
结合 async await
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script src="js/axios.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<button @click='getInfo'>GET</button>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
methods: {
async getInfo() {
const result = await axios.get('http://www.liulongbin.top:3005/api/get', {
params: {
name: 'zs',
age: 20
}
});
console.log(result);
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
解构赋值
const user = {
name: 'zs',
age: 20,
gender: 'man'
}
// 把name属性解放出来,当作常量去使用。
// const { name } = user
// console.log(name);
// 给age取别名:userage
const { name, age: userage } = user
console.log(name, userage);
这样我们获取数据的时候,就可以用解构赋值,只得到我们想要的那部分数据了!
async function getInfo() {
const {data:retVal} = await axios.get('http://www.liulongbin.top:3005/api/get', {
params: {
name: 'zs',
age: 20
}
});
console.log(result);
}
post请求
async postInfo() {
const { data: retVal } = await axios.post('http://www.liulongbin.top:3005/api/post', { name: 'ls', gender: 'man' })
console.log(retVal.data);
}
Vue推荐用法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script src="js/axios.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<button @click='getInfo'>GET</button>
<button @click='postInfo'>POST</button>
</div>
<script>
// 通过这个属性,全局设置 请求的 根路径。
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://www.liulongbin.top:3005'
Vue.prototype.$http = axios;
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
methods: {
async getInfo() {
// 请求数据的时候会。 baseURL + 路径 = 'http://www.liulongbin.top:3005' + '/api/get'
const { data: retVal } = await this.$http.get('/api/get', {
params: {
name: 'zs',
age: 20
}
});
console.log(retVal.data);
},
async postInfo() {
const { data: retVal } = await this.$http.post('/api/post', { name: 'ls', gender: 'man' })
console.log(retVal.data);
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
axois的传参
this.$http.get('/user/10',{params:{name:'zs',age:22}}) // ===> http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/10?name=zs&age=2
案例
带有数据库的品牌管理案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script src="js/axios.js"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/bootstrap.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="panel panel-primary inline">
<div class="panel-heading inline">
<h3 class="panel-title">添加新品牌</h3>
</div>
<div class="panel-body form-inline">
<div class="input-group">
<div class="input-group-addon">品牌名称</div>
<input type="text" class="form-control" v-model='name'>
</div>
<div class="input-group">
<button class="btn btn-primary" @click='add'>添加</button>
</div>
<div class="input-group">
<div class="input-group-addon">按名称搜索</div>
<input type="text" class="form-control" v-model='keywords'>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<table class="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>name</th>
<th>time</th>
<th>operate</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<!-- 很巧妙啊 in search() search用来过滤 -->
<tr v-for="item in search()" :key='item.id'>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td></td>
<td><a href="#" @click.prevent="remove(item.id)">删除</a></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</body>
<script>
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://liulongbin.top:3005';
Vue.prototype.$http = axios;
// 定义全局过滤器
Vue.filter('dataFormat', function (originVal) {
const dt = new Date(originVal);
const y = dt.getFullYear();
const m = (dt.getMonth() + 1 + '').padStart(2, '0');
const d = (dt.getDay() + '').padStart(2, '0');
return `${y}-${m}-${d}`
})
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
brandList: [],
name: '',
keywords: ''
},
created() {
//在created中发起首屏数据的请求
this.getBandList()
},
methods: {
async getBandList() {
const { data: res } = await this.$http.get('/api/getprodlist');
// console.log(res);
// return res.message; 返回的是一个promise对象。
// 应该这么写
this.brandList = res.message;
},
async add() {
const { data: res } = await this.$http.post('/api/addproduct', { name: this.name });
if (res.status !== 0) return alert('添加失败!');
this.getBandList();
this.name = '';
},
search() {
return this.brandList.filter(item=>item.name.includes(this.keywords))
},
async remove(id) {
const { data: res } = await this.$http.get('/api/delproduct/' + id);
if (res.status !== 0) return alert('删除失败');
else this.getBandList();
}
}
});
</script>
</html>
Demo
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<style>
/* 定义入场之前和离场之后的样式 */
.v-enter,
.v-leave-to {
transform: translateX(150px);
}
/* 定义入场阶段和离场阶段的样式 */
.v-enter-active,
.v-leave-active {
transition: all 0.8s ease;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<button @click='flag=!flag'>toggle</button>
<!-- 1.使用vue提供的transition标签 包裹需要添加动画的元素 name默认以v为前缀。 -->
<transition name='v'>
<h3 v-if='flag'>asfaf</h3>
</transition>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: { flag: true },
methods: { }
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
三方动画库
Vue 不支持 animate4.0
- 把需要添加动画的元素,使用 v-if 或 v-show 进行控制。
- 把需要添加动画的元素,使用 Vue 提供的元素
<transition></transition>包裹起来 - 为
<transition></transition>添加两个属性类enter-active-class,leave-active-class - 把需求添加动画的元素,添加一个 class=’animated’
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/animate.min.css">
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<button @click='flag=!flag'>toggle</button>
<!-- 1.使用vue提供的transition标签 包裹需要添加动画的元素 -->
<transition enter-active-class="bounceInDown" leave-active-class="bounceOutDown">
<h3 v-show='flag' class="animated">aasffasfsasfasfsfaf</h3>
</transition>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
flag: true
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
v-for的列表过渡
-
把 v-for 循环渲染的元素,添加
:key属性【注意:如果为列表项添加动画效果,一定要指定 key,并且,key 的值不能为索引】 -
在 v-for 循环渲染的元素外层,包裹
<transition-group>标签 -
添加两组类即可:
.v-enter,
.v-leave-to{
opacity:0,
transform:translateY(100px);
}
.v-enter-active,
.v-leave-active{
transition:all 0.8s ease;
}
具体 Demo
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/animate.min.css">
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input v-model="name"> <button @click="add">添加</button>
<!-- 默认会用span 包裹 li。我们指定tag的话,就会用我们指定的tag包裹 -->
<transition-group tag='ul' enter-active-class="bounceInDown" leave-active-class="bounceOutDown">
<li v-for="item in list" :key="item.id" @click="del(item.id)" class="animated"></li>
</transition-group>
</div>
</body>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
list: [
{ "id": 1, "name": 'd1' },
{ "id": 2, "name": 'd2' },
{ "id": 3, "name": 'd3' }
],
newId: 4,
name: "123"
},
methods: {
add() {
const newInfo = { "id": this.newId++, "name": this.name }
console.log(name);
this.list.push(newInfo);
this.name = ''
},
// 有问题,不过没事,就了解一下。
del(id) {
const i = this.list.findIndex(item=>item.id===id);
this.list.splice(i, 1);
}
},
})
</script>
</html>
SPA
component组件
通过 component 的 is 属性,动态指定要渲染的组件。
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>App 根组件</h1>
<!-- 注意 是字符串 'GG' 按字符串名称来搜索的! -->
<component :is="'GG'"></component>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import Parent from "@/components/Father2Son/Parent";
import GG from '@/components/Son2Son/GG'
import DD from '@/components/Son2Son/DD'
import Vue from "vue";
Vue.component('GG', GG)
Vue.component('DD', DD)
export default {}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>App 根组件</h1>
<button @click="comName='GG'">GG</button>
<button @click="comName='DD'">DD</button>
<!-- 注意 是字符串 'GG' 按字符串名称来搜索的! -->
<component :is="comName"></component>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import Parent from "@/components/Father2Son/Parent";
import GG from '@/components/Son2Son/GG'
import DD from '@/components/Son2Son/DD'
import Vue from "vue";
Vue.component('GG', GG)
Vue.component('DD', DD)
export default {
data() {
return {
comName: 'GG'
}
},
methods: {}
}
</script>
锚链接及常规url的区别
1.普通的 URL 地址:会刷新整个页面;会追加浏览历史记录;
2.锚链接:不会触发页面的整体刷新;会追加浏览历史记录;(锚链接时页面内的跳转)
SPA相关概念
- 概念定义:SPA –> Single Page Application,单页面应用程序;即只有一个Web页面的网站,网站的所有功能都在这个唯一的页面上进行展示与切换。
- 特点
- 只有一个页面
- 浏览器一开始请求这个页面,必须加载对应的 HTML,CSS,JavaScript
- 用户的所有操作,都在这唯一的页面上完成
- 页面数据都是用Ajax请求回来的
- 好处
- 实现了前后端分离开发,各司其职;提高了开发效率;
- 用户体验好、快,内容的改变无需重新加载整个页面;
- 缺点
- 对 SEO 不是很友好,因为页面数据是 Ajax 渲染出来的;(SSR)服务器端渲染;
- 刚开始的时候加载速度可能比较慢;项目开发完毕后,可以单独对首屏页面的加载时间做优化;
- 页面复杂的比较高,对程序员的能力要求较高;
原始实现SPA
使用 component 标签的 :is 属性来切换组件
总结:单页面应用程序中,实现组件切换的根本技术点,就是==监听 window.onhashchange 事件==;
- window.location.hash 获得 hash 值
- window.onhashchange 监听 hash 的变化
- 能用
=>函数就用,可以解决this的指向问题
路由
路由常用属性
- path 要匹配的 hash 地址
- component 要展示的组件
- redirect 要重定向到的地址
- props 开启 props 传参
- children 嵌套路由
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 创建路由规则
const router = new VueRouter({
// 路由规则的数组
routes: [
// 每一个路由规则,都是一个对象,这个对象中,必须有 path 属性和 component 属性
// 其中path 是 hash 地址,component 是前面 hash 地址对应要展示的组件。
{path: '/home', component: Home},
{path: '/about', component: About},
// 在某个路由规则中嵌套子路由规则? path.component有个同级属性 children属性
{
path: '/movie',
component: Movie,
children: [{path: '/movie/tab1', component: tab1}, {path: '/movie/tab2', component: tab2}]
},
{path: '/', component: About},
],
linkActiveClass: 'my-active'
})
什么是路由
路由就是对应关系;
- 后端路由的定义:URL 地址到后端处理函数之间的关系
- 前端路由的定义:hash 到组件之间的对应关系
- 前端路由的目的:为了实现单页面应用程序的开发
- 前端路由的三个组成部分
- 链接
- 组件
- 链接 和 组件之间的对应关系
Vue中使用 vue-router ★
安装导入并注册路由模块
-
运行 npm i vue-router -S 安装路由模块
-
在 index.js 导入并注册路由模块
// 导入路由模块 import VueRouter from 'vue-router' // 注册路由模块 Vue.use(VueRouter)
创建路由链接
<!-- router-link 就是 第一步,创建路由的 hash 链接的 -->
<!-- to 属性,表示点击此链接,要跳转到哪个 hash 地址,注意:to 属性中,大家不需要以 # 开头 -->
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/move">电影</router-link>
创建并在 main.js 中导入路由相关组件
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Home from '@/components/router/Home'
import About from '@/components/router/About'
import Movie from '@/components/router/Movie'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 创建路由规则
const router = new VueRouter({
// 路由规则的数组
routes: [
// 每一个路由规则,都是一个对象,这个对象中,必须有 path 属性和 component 属性
// 其中path 是 hash 地址,component 是前面 hash 地址对应要展示的组件。
{ path: '/home', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About },
{ path: '/movie', component: Movie },
{ path: '/', component: About },
]
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
// 指定路由规则对象
router: router
}).$mount('#app')
创建路由规则
// 创建路由规则
const router = new VueRouter({
// 路由规则的数组
routes: [
// 每一个路由规则,都是一个对象,这个对象中,必须有 path 属性和 component 属性
// 其中path 是 hash 地址,component 是前面 hash 地址对应要展示的组件。
{path: '/home', component: Home},
{path: '/about', component: About},
{path: '/movie', component: Movie},
{path: '/', component: About},
]
})
在页面上放路由容器
<!-- 这是路由容器,将来通过路由规则,匹配到的组件,都会被展示到这个 容器中 -->
<router-view></router-view>
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>App 根组件</h1>
<hr>
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">关于</router-link>
<router-link to="/movie">电影</router-link>
<!-- 路由容器组件,路由匹配到的组件 会被替换到 router-view里显示 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
路由高亮
- 方法一:通过路由默认提供的 router-link-activate,为这个类添加自己的高亮样式即可
<style scoped>
.router-link-active {
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
- 方法二:通过路由构造函数,在传递路由配置对象的时候,==提供 linkActivateClass 属性==,来覆盖默认的高亮类样式。适用于:用到的 UI组件库中提供了默认的高亮效果。
const router = new VueRouter({
// 路由规则的数组
routes: [
// 每一个路由规则,都是一个对象,这个对象中,必须有 path 属性和 component 属性
// 其中path 是 hash 地址,component 是前面 hash 地址对应要展示的组件。
{path: '/home', component: Home},
{path: '/about', component: About},
{path: '/movie', component: Movie},
{path: '/', component: About},
],
// 用到的 UI组件库中提供了默认的高亮效果,用这个
linkActiveClass: 'my-active'
})
嵌套路由
App.vue有 <router-link to="/movie">电影</router-link>和<router-view></router-view>
App.vue 下的 Move.vue 也有,那么路由的写法如下:
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Home from '@/components/router/Home'
import About from '@/components/router/About'
import Movie from '@/components/router/Movie'
import tab1 from '@/components/router/tab/Tab1'
import tab2 from '@/components/router/tab/Tab2'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 创建路由规则
const router = new VueRouter({
// 路由规则的数组
routes: [
// 每一个路由规则,都是一个对象,这个对象中,必须有 path 属性和 component 属性
// 其中path 是 hash 地址,component 是前面 hash 地址对应要展示的组件。
{path: '/home', component: Home},
{path: '/about', component: About},
// 在某个路由规则中嵌套子路由规则? path.component有个同级属性 children属性
{
path: '/movie',
component: Movie,
children: [{path: '/movie/tab1', component: tab1}, {path: '/movie/tab2', component: tab2}]
},
{path: '/', component: About},
],
linkActiveClass: 'my-active'
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
// 指定路由规则对象
router: router
}).$mount('#app')
redirect 重定向
在路由规则中,通过 redirect 属性,指向一个新地址,就能够实现路由的重定向
// 创建路由规则
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
// 重定向,实现根地址的默认选择
{ path: '/', redirect: '/home' },
{ path: '/home', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About },
{
path: '/movie',
component: Movie,
redirect: '/move/tab1'
children: [ { path: '/movie/tab1', component: tab1 }, { path: '/movie/tab2', component: tab2 } ]
},
],
linkActiveClass: 'my-active'
})
路由传参
在路由后面加上冒号实现路由传参。
==当 router-link 的 to 地址,要动态进行拼接的时候,一定要把 to 设置呈属性绑定的形式==
<template>
<div> <ul> <router-link tag="li" v-for="item in mlist" :key="item.id" :to="'/mdetail/' +item.id"> </router-link> </ul> </div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MoveList",
data() {
return {
mlist: [
{ id: 1, name: '雷神' },
{ id: 2, name: '死侍' },
{ id: 3, name: '钢铁侠' },
]
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
li {
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import MoveList from "@/components/router/MoveList";
import MoveDetail from "@/components/router/MoveDetail";
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/', component: MoveList },
// 把路由规则中,参数项位置,前面加上 : 表示这是一个参数项
{ path: '/mdetail/:id', component: MoveDetail },
]
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
// 指定路由规则对象
router: router
}).$mount('#app')
模板字符串传递参数
<router-link tag="li" v-for="item in mlist" :key="item.id" :to='`/mdetail/${item.id}/${item.name}`'> </router-link>
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/', component: MoveList },
{ path: '/mdetail/:id', component: MoveDetail },
{ path: '/mdetail/:id/:name', component: MoveDetail },
]
})
获得路由参数
思路
路由规则中开启路由传参数 ==props:true==
页面设置 props 属性接收数据 ==props:[‘id’,’name’]==
props:[] 外界传递过来的数据,数据都是只读的。
代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import MoveList from "@/components/router/MoveList";
import MoveDetail from "@/components/router/MoveDetail";
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/', component: MoveList },
// props true 表示,为当前路由规则,开启 props 传参
{ path: '/mdetail/:id/:name', component: MoveDetail, props: true },
]
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
// 指定路由规则对象
router: router
}).$mount('#app')
获得参数
<template>
<div>
电影详情
<h4>==</h4>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MoveDetail",
// 接收 路由传递过来的参数
props: ['id', 'name']
}
</script>
其它方式:不推荐使用!
直接使用 this.$route.params 来获取参数;写起来太麻烦,不推荐。
命名路由
什么是命名路由:就是为路由规则,添加了一个 name。
思路
为路由添加一个 name 属性,如name:'movedetail'
在 router-link 添加 :to="{name:'movedetail',params:{id:item.id,name:item.name}}"
代码示例
<router-link tag="li" v-for="item in mlist" :key="item.id" :to="{name:'movedetail',params:{id:item.id,name:item.name}}"></router-link>
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import MoveList from "@/components/router/MoveList";
import MoveDetail from "@/components/router/MoveDetail";
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/', component: MoveList },
// props true 表示,为当前路由规则,开启 props 传参
{ path: '/mdetail/:id/:name', component: MoveDetail, props: true,name:'movedetail' },
]
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
// 指定路由规则对象
router: router
}).$mount('#app')
编程式(JS)导航
概念普及
之前所学的 router-link 是标签跳转
除了使用 router-link 是标签跳转之外,还可以使用 JavaScript 来实现路由的跳转
什么是编程式导航:使用 vue-router 提供的 JS API 实现路由跳转的方式,叫做编程式导航;
编程式导航的用法:
this.$router.push('路径的地址')this.$router.go(n)this.$router.forward()this.$router.back()
this.$route 路由参数对象
this.$router 是路由导航对象
vm 实例上的 router 属性,是来挂载路由对象的
在 new VueRouter({/* 配置对象 */}) 的时候,配置对象中,有一个 routes 属性,是来创建路由规则的。
跳转路由
思路
为标签绑定点击事件:@click="getDetail"
点击事件中使用:this.$router.push(`/mdetail/${item.id}/${item.name}`)js /mdetail 是路由地址,后面的是传过去的参数
参数接收的方式 还是通过 props
代码
<template>
<div> <li tag="li" v-for="item in mlist" :key="item.id" @click="getData(item)"> </li> </div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "JSDaoHan",
data() {
return {
mlist:
[ {id: 1, name: '雷神'},
{id: 2, name: '死侍'},
{id: 3, name: '钢铁侠'},]
}
},
methods: {
getData(item) {
this.$router.push(`/mdetail/${item.id}/${item.name}`)
}
}
}
</script>
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/', component: JSDaoHan },
// props true 表示,为当前路由规则,开启 props 传参
{ path: '/mdetail/:id/:name', component: MoveDetail, props: true },
]
})
路由后退
- this.$router.back() 退后一步
- this.$router.go(-1) -1 退后一步,-2 退后两步
- this.$router.go(-1) -1 退后一步,-2 退后两步
- this.$router.forward() 前进一步
路由导航守卫
介绍
检测用户有无权限!提供了一层拦截!
案例需求:只允许登录的情况下访问 后台首页,如果不登录,默认跳转回登录页面;
API 语法
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/', component: JSDaoHan },
{ path: '/mdetail/:id/:name', component: MoveDetail, props: true },
]
})
// 在访问这个路由对象,每一个路由规则之前,都需要先调用 指定的回调函数,如果回调函数放行了,就看得到想看的组件,反之,就无法看到。
// to: 是要去的哪个页面路由相关的参数
// from: 从哪个页面即将离开
// next: 一个函数,相对于 node 里面 express 中的 next 函数
router.beforeEach( (to, from, next)=>{ /* 导航守卫 处理逻辑 */ } )
实现登录拦截
路由代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Login from "@/components/routerShouWei/Login";
import Home from "@/components/routerShouWei/Home";
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/', redirect: '/login' },
{ path: '/login', component: Login },
{ path: '/home', component: Home },
]
})
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
// to.path 表示我们下一刻要访问哪个地址
// from.path 表示我们上一刻,所访问的是哪个地址
// 如果访问 /login 说明要登录,没必要拦截
if (to.path === '/login') return next()
// 拿到 token 看用户是否登录
const token = window.sessionStorage.getItem('user')
// 未登录则跳转到登录页面
if (!token) return next('/login')
// 登录了则放行
next()
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
// 指定路由规则对象
router: router
}).$mount('#app')
登录页面
<template>
<div>
<p>姓名:<input type="text" v-model="name"></p>
<p>密码:<input type="text" v-model="password"></p>
<button @click="login">登录</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Login",
data() {
return {
'name': '',
'password': ''
}
},
methods: {
login() {
if (this.name == "123" && this.password == "123") {
// 登录成功保存token
// eslint-disable-next-line no-unused-vars
const token = "sfasfjaskfaskfhaasjkfhasjkfhaskfasfs";
window.sessionStorage.setItem("user", token)
this.$router.push("/home")
} else {
alert("用户名 或 密码错误")
}
}
}
}
</script>
登录后的页面
<template>
<div> <h3>后台主页,不等于不允许访问!</h3> </div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home"
}
</script>
案例
数据列表组件
<template>
<div>
<h1>品牌列表案例</h1>
<el-button type="primary" @click="addDialogShow">添加新品牌</el-button>
<!-- 品牌列表数据 -->
<el-table :data="brandList" border stripe style="width:100%">
<el-table-column type="index" label="索引" width="100%"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="id" label="编号"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="name" label="品牌名称"></el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="ctime" label="创建时间">
<template slot-scope="scope">
</template>
</el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="操作">
<template slot-scope="scope">
<!-- 如果在 表格的 column 渲染数据,必须使用 作用域插槽才行 -->
<el-button type="primary" :search="scope.row.id">查询</el-button>
<el-button type="success" :search="scope.row.id">修改</el-button>
<el-button @click="deleteData(scope.row.id)" type="danger" :search="scope.row.id">删除</el-button>
</template>
</el-table-column>
</el-table>
<!-- 添加新品牌的对话框 -->
<el-dialog title="添加品牌" :visible.sync="add" width="50%">
<el-form :model="addForm" :rules="addFormRules" ref="addFormRef" label-width="100px">
<el-form-item label="品牌名称" prop="name">
<el-input v-model="addForm.name" v-focus></el-input>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
<span slot="footer" class="dialog-footer">
<el-button @click="add = false">取 消</el-button>
<el-button type="primary" @click="addNewBrand">确 定</el-button>
</span>
</el-dialog>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "BrandList",
data() {
return {
// 品牌列表数据
brandList: [
{id: 1, name: '123', ctime: '2020-11-11'},
{id: 2, name: '1234', ctime: '2020-11-5'}
],
add: false,
addForm: {
name: '',
ctime: new Date()
},
addFormRules: {
name: [
{required: true, message: '请输入活动名称', trigger: 'blur'},
{min: 2, max: 55, message: '长度在 2 到 55 个字符', trigger: 'blur'}
]
}
}
},
methods: {
async getBrandList() {
const {data: res} = await this.$http.get("/api/getprodlist")
if (res.status != 0) return alert("数据获取失败")
// 数据获取成功
this.brandList = res.message
},
addDialogShow() {
this.add = true
},
addDialogClosed() {
this.$refs.addFormRef.resetFields()
},
addNewBrand() {
this.$refs.addFormRef.validate(async valid => {
if (!valid) return
const {data: res} = await this.$http.post('/api/addproduct', {name: this.addForm.name})
if (res.status !== 0) return this.$message.error("添加失败!")
this.$message.success("添加成功!")
this.add = false
this.getBrandList()
})
},
// 删除
async deleteData(id) {
const data = await this.$confirm('此操作将永久删除该文件, 是否继续?', '提示', {
confirmButtonText: '确定',
cancelButtonText: '取消',
type: 'warning'
}).catch(err => err)
if (data !== 'confirm') return this.$message.error("取消删除")
const {data: res} = await this.$http.get("/api/delproduct/" + id)
if (res.status !== 0) return this.$message.error("删除失败")
this.$message.success("删除成功")
this.getBrandList()
}
},
created() {
this.getBrandList();
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.el-button {
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
</style>
根组件数据展示
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App'
}
</script>
路由配置
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import Router from "vue-router"
import BrandList from "./components/BrandList";
import axios from "axios"
import ElementUI from 'element-ui';
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css';
Vue.use(ElementUI);
axios.defaults.baseURL = "http://www.liulongbin.top:3005"
Vue.prototype.$http = axios
Vue.use(Router)
const routes = new Router({
routes: [
{path: '/', component: BrandList}
],
mode: 'hash'
})
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 定义全局过滤器
Vue.filter('dataFormat', (originVal) => {
const dt = new Date(originVal)
const y = dt.getFullYear();
const m = (dt.getMonth() + 1 + '').padStart(2, '0');
const d = (dt.getDate() + '').padStart(2, '0');
return `${y}-${m}-${d}`
})
// 定义全局聚焦指令
Vue.directive('focus', {
// 当被绑定的元素插入到 DOM 中时……
inserted: function (el) {
// 聚焦元素
console.log(el);
el.children[0].focus()
}
})
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
router: routes
}).$mount('#app')
app打包需要添加这个 vue.config.js
防止打包后的页面一片空白。
vue的路由模式需要改为 mode: 'hash',保证路由可正确跳转。
module.exports = {
assetsDir: 'static',
parallel: false,
publicPath: './',
}
执行打包命令 npm run build 打包到了 dist 文件下,用 HBuilder 创建一个 H5+APP 的项目,把 dist 中的内容拷贝过去,然后打包为 app 。
项目中的问题
骨架屏
Vue页面骨架屏 - SegmentFault 思否 可以用 vv-ui
图片过大,上传过慢
Vue+Vant 压缩图片,提高上传速度。
<van-uploader :max-size="4 * 1024 * 1024" capture="camera" class="uploader" accept="image/*"
:after-read="afterRead">
<van-swipe-item>
<van-button plain type="info" icon="plus" class="re-btn">
拍照识别
</van-button>
</van-swipe-item>
</van-uploader>
// base64 转 file
dataURLtoFile(dataurl, filename) {
var arr = dataurl.split(','), mime = arr[0].match(/:(.*?);/)[1],
bstr = atob(arr[1]), n = bstr.length, u8arr = new Uint8Array(n);
while (n--) {
u8arr[n] = bstr.charCodeAt(n);
}
return new File([u8arr], filename, {type: mime});
},
afterRead(file) {
console.log(file)
// 图片大于500kb就压缩
if (file.file.size > 512000) {
let canvas = document.createElement('canvas') // 创建Canvas对象(画布)
let context = canvas.getContext('2d')
let img = new Image()
img.src = file.content // 指定图片的DataURL(图片的base64编码数据)
let files = file;
img.onload = () => {
let size = files.file.size / 512000
canvas.width = img.naturalWidth / Math.sqrt(size)
canvas.height = img.naturalHeight / Math.sqrt(size)
context.drawImage(img, 0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height)
files.content = canvas.toDataURL(files.file.type, 0.92) // 0.92为默认压缩质量
let myFile = this.dataURLtoFile(files.content, files.file.name)//dataURLtoFile为自己封装的函数,将base64转为file
console.log(files)
let formDatas = new FormData()
formDatas.append('file', myFile)
this.upload(formDatas)//上传的封装函数
}
} else { //小于10M直接上传
let formData = new FormData()
formData.append('file', file.file)
console.log(formData)
this.upload(formData)//上传的封装函数
}
},
async upload(formData) {
const {data: response} = await this.$http.post('/upload', formData)
if (response.code == 200) {
Toast.success(response.msg);
window.sessionStorage.setItem("classify_result", JSON.stringify(response))
window.sessionStorage.getItem("classify_result")// 此处获得 图片回显的 url 地址。
this.$router.push("/result/classify")
} else {
Toast.fail(response.msg);
}
},
axios 等网络请求出现异常
try{
// 处理异常,才发现 js 有 try catch
}catch(error){
}
// =====================
async upload(formData) {
try {
const {data: response} = await this.$http.post('/upload', formData)
if (response.code == 200) {
Toast.success(response.msg);
window.sessionStorage.setItem("classify_result", JSON.stringify(response))
window.sessionStorage.getItem("classify_result")// 此处获得 图片回显的 url 地址。
this.$router.push("/result/classify")
} else {
Toast.fail(response.msg);
}
} catch (error) {
Toast("请求未响应,请检查网络是否正常!");
}
}
跨域问题
后端已经允许跨域了,也响应成功了,但是前端无法接受到数据,提示跨域错误。(为什么?好像是前端接受数据的时候发现后端传过来的数据和自己不是同源,所以依旧是跨域错误,取消凭证即可)
axios.defaults.crossDomain = false
axios.defaults.withCredentials = false // 不用凭证
axios.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type'] = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'